Introduction
Electro-Mechanical Protection relays are now things of the past. Those can be seen in old installations or small electrical network with cost constraint. All new electrical systems are fitted with Numerical Protection relays now-a-days.
Let's see how easily such relays can be checked / tested for healthy measurement and protection function working. Testing is generally carried out during commissioning of new systems or as a part of annual testing required to ensure healthiness and proper working of relays which are in service.
Over current Protection Function
Over current is most basic protection which are used in Incomers, Bus couplers and outgoing feeders which are acting as source for another switch gear / system. This is also used as a backup protection in case of transformers and transmission lines. Sometimes, over current protection is used for protecting motor from short circuits.
This protection is generally of 3 types :
- Instantaneous Over current
- Definite Time Over current
- Inverse Time Over current
Instantaneous Over Current Protection
Relay will issue trip when the current increases over set trip current value (i.e. pick up value, Ipickup) instantaneously. Practically, there will be some time delay, in Milli seconds which may vary relay to relay.
ANSI device number for this protection is 50. In this protection function, we only need to set one parameter which is 'Pick up Current'.
Definite Time Over Current Protection
For relay to issue trip, Current must be above set pickup current (Ipickup) for the period of set time delay (td). If current decreases below Ipickup before time delay is reached, the relay will not issue trip command. Trip time will always be equal to time delay (td) set, irrespective of actual current as long as it is above Ipick, that's why, Definite Time (DT).
ANSI device number for this protection is 50. In this protection function, we have to set 'Pick up current' and 'Time Delay'.
Inverse Time Over Current Protection
In this protection, trip time will be inversely proportional to the actual current. Time will be less for large fault currents and vice versa.
ANSI device number for this protection is 51. In this protection function, we have to set 'Pick up current', 'Curve Type' and 'Time Delay'.
There are basic three type of curves
- Standard Inverse
- Very Inverse
- Extremely Inverse
There is also forth type of curve known as Inverse Definite Minimum Time ( IDMT) wherein trip time will be constant after certain amount of fault current.
Before commencing testing of numerical relay, ensure following
- CT Ratio is properly set
- Over current protections is enabled and settings are saved
- Trip relay assigned to the over current protection and related terminals for trip feedback.
Identify the correct terminals for CT input and connect relay test set Current outputs to these terminals. Connect trip contact terminals of the relay to the Binary input of the test set. Enable trigger stop on the connect binary I out in the test set software.
Very first step of testing numerical relays is to verify measurement function of the relays. This confirms that relay is measuring the injected current through test set according to CT ratio. Disable all current based protections to avoid tripping by the relay.
If CT ratio set is 800/1A, it must read 800A in the relay upon injection of 1A. Measured value may vary depending upon quality of supply to the test set, accuracy of the relay and test set. Reading in relay then will display value like 798A or 805A.
To avoid such fluctuations / deviations, we must use UPS or voltage stabilizer for supplying test set. And also, calibrated test set must be used where the errors are known and can be accounted for the reading in relay.
Testing of Instantaneous and DT Type Over current Protection
- Enable over current protection and note down settings. Disable other current based protections.
- For instantaneous protection, there will no time delay setting. In case of DT protection, time delay setting will be available.
- Now inject current in R phase with value below Ipickup. e.g. If Ipickup is 1 amp, then set current in test set as 0.9A for R phase and 0A in remaining phases.
- Make sure that trigger stop is enabled on binary input connected to relay trip contact.
- Start injection with set current in test set. Increment current in step of either 0.1 or 0.01 or 0.001 as per your requirement of correctness. Time required for the test will be more for 0.001 step than it is for 0.1 step. Set your start point accordingly.
- Now, Increment current in once in step set. Make sure to keep delay between two increments equal to time delay setting plus 2 seconds.
- Auto increment function are available in the modern test sets wherein we can set step delay as set in above point. Test will stop automatically when relay issues trip command is trigger stop is enabled in test set software.
- Increment current till relays issues trip on over current. Note down Current at which trip is issued and also trip time from test set.
- Pick up current must be equal to Ipickup setting of the relay. Trip time will in between 20 to 40mSec in case of instantaneous over current. For DT over current, trip time must be equal to time delay setting of the protection function. It might be higher by 20 to 40mSec depending on and and type of relay. This time delay in milliseconds is relay response time from change in input current above pickup value to operation of electro-mechanical relay inside numerical relay used for potential free contact as output.
- Once pick up current is verified, inject twice the pick up current and check for trip time. Trip time must be approximately equal to trip time reading from the step 8.
- Sometimes relay makes chattering sound when injected current is near to pickup current value. This noise is of electro-mechanical relay continuously operating since relay is sensing current changing around pick up value. When current is above pickup value, relay picks up. It drops when current goes below. It creates chattering sound. We have to keep incrementing current in step till relay is trip indication is ON and chattering will stop. This chattering is more likely to be observed when steps are small, like 0.001A. With bigger steps, this problem may not occur.
- Repeat the steps 3 to 8 for remaining phases and verify the pick up currents and trip time. Ideally, all readings should match.
- Carry out same test for 3 phases.
Testing of Inverse Time Over current Protection
- Enable over current protection and note down settings. Disable other current based protections
- For checking correctness of the trip time of the relay, we need to calculate the trip time in advance to compared it with test result.
I'll create another blog on Trip time calculation on Inverse Characteristic in near future. Till then, you can download & use my android app "Electrical Protection Calci" which is free to use for required calculation.
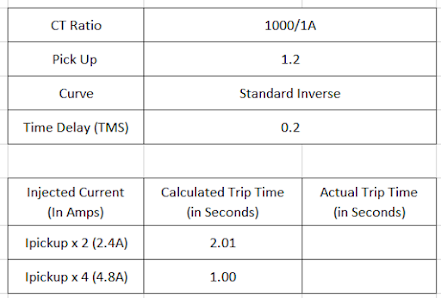
- Following table shows example calculation for Standard Inverse Curve
- Inject 2.4 Amps in R phase. Note down trip time from Test set software. It must be approximately equal to 2.01 seconds. Similarly, for 4.8A, trip time will be equal to 1 sec.
Sample Test Report
Any doubts / corrections / suggestions are welcome through comments or feel free to contact me through e-mail.
Bye for now 🙏




Nice 👍
ReplyDeleteHelpful to improve skills... Nice sir.
ReplyDeleteMine too
DeleteThank you Sir,very helpful information
ReplyDeleteThanks Jagga
DeleteGood Start sir, it is a firm step to share experience and knowledge. Thanx for this. Please go ahead and keep sharing the gyan you earned.👍
ReplyDeleteThank you Sanket
DeleteVery informative.
ReplyDeleteStraight and simple
ReplyDeleteVery well explained Swapnil 👍🏻👍🏻
Thank you Akshay
DeleteThanks 😊
ReplyDeleteJabardast
ReplyDeleteThanks Sandy!
DeleteAwesome, that what you have mastery in.. good going
ReplyDeleteThank you
DeleteGood yaar. Nice way of explanation and nice platform.
ReplyDeleteThanks Umesh
DeleteRespected sir
ReplyDeletePlease explain short circuit test of 1600KVA , 11KV/6.6 KV,Dyn11, %Z=6%
We need to apply (11000x0.06) voltage at HV side to achieve rated current in LV side. Measure Applied voltage, current and power drawn at HV side. With these parameters, we can find out R, X and Z along with copper loss of transformer. Hope this satisfies you requirement
DeleteHi, very and good explanation thank you. Wht about distance relay testing
ReplyDeleteHi thr, never tested distance protection. But, I'll post as soon as i get a chance. Keep reading
Delete